
Multi-Factor Authentication
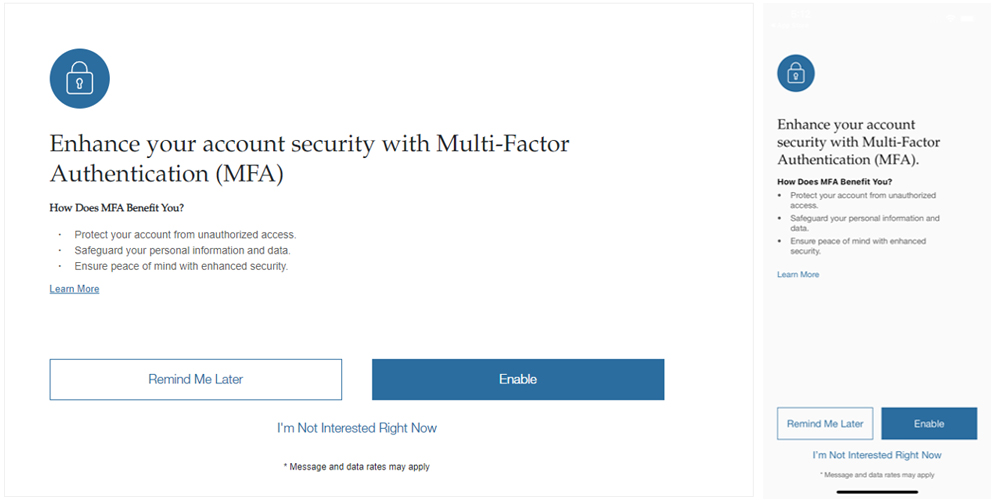
Enhance Your Account Security with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Oppenheimer uses Multi-Factor Authentication on both the Client Access Web Portal and the Oppenheimer Mobile App to provide an additional layer of security.
Click here to view the Client Access Agreement.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
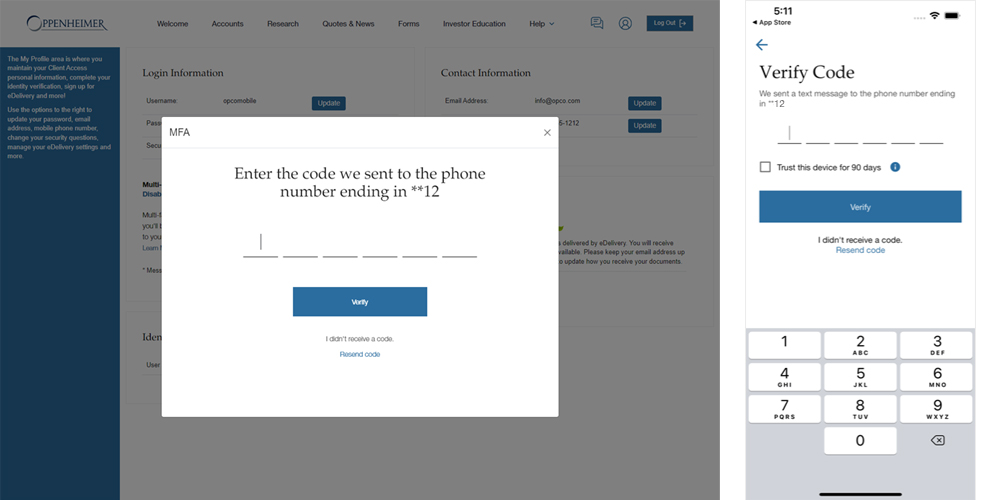
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a multi-step process that requires users to enter more information than just their password. Along with the password, users will be asked to enter a code sent to their mobile device. A second form of authentication like this can help prevent unauthorized account access if the user’s password has been compromised.
This code will remain valid for 5 minutes. If the code expires, you can click on “Resend Code.” Do not share this with anyone. We will never contact you to request this code.
How Does Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Benefit Users?
- Protects your account from unauthorized access.
- Safeguards your personal information and data.
- Ensures peace of mind with enhanced security.
How to Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
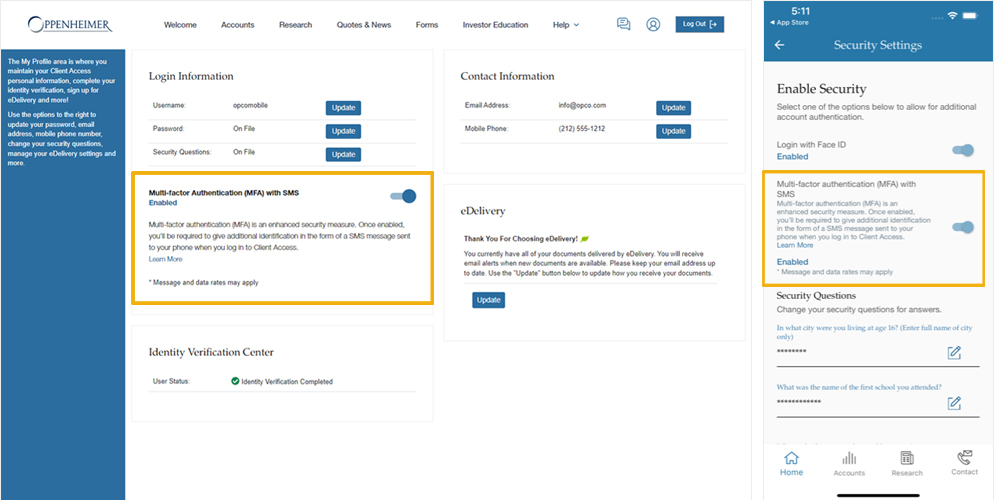
Web-users have the ability to navigate to their profile and turn on MFA at any time. In order to do this, the user must first have a mobile phone number on file. Users will be prompted to enter this missing information before enabling MFA. The user will receive MFA prompts upon login, while trying to reset a password, and when updating important profile fields.
If you intend to use MFA with the Opco Mobile app, please make sure your app is updated to the latest available version. Older versions of the mobile app do not support MFA and you will be unable to use the mobile app once you enable MFA on the website.
Mobile app users can navigate to “My Profile” and select “Security Settings.” To enable MFA, simply set the status to Enabled. The same prompts will follow as those of web-users discussed above.
By enabling Multi-Factor Authentication on the Client Access Web Portal and the Oppenheimer Mobile App, you are agreeing to the Multifactor Authentication Terms and Conditions.
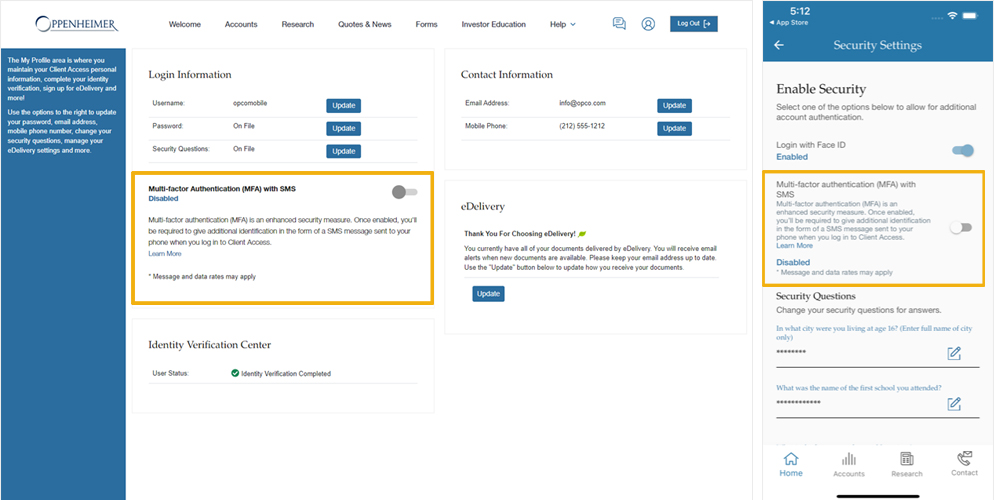
How to Disable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
To disable MFA, web-users can navigate to “My Profile” and set their MFA status to Disabled.
Mobile app-users can navigate to “My Profile” and select “Security Settings” and set their MFA status to Disabled.
What is a Trusted Device?
A trusted device is one that's given permission to access certain accounts or services without extra verification steps like passwords or codes. If you enable MFA on your online account, you may designate your personal mobile device or computer as a trusted device.
After logging in and verifying your identity through a secondary method (like a code sent to your phone), the system remembers your device. For 90 days, you'll have hassle-free access to your accounts from that device, as long as you've also activated multi-factor authentication (MFA). It's a balance between security and convenience, making login processes smoother.
To enhance security, under certain circumstances your devices will become un-trusted when major updates are made to contact information i.e., email address, password change, etc.
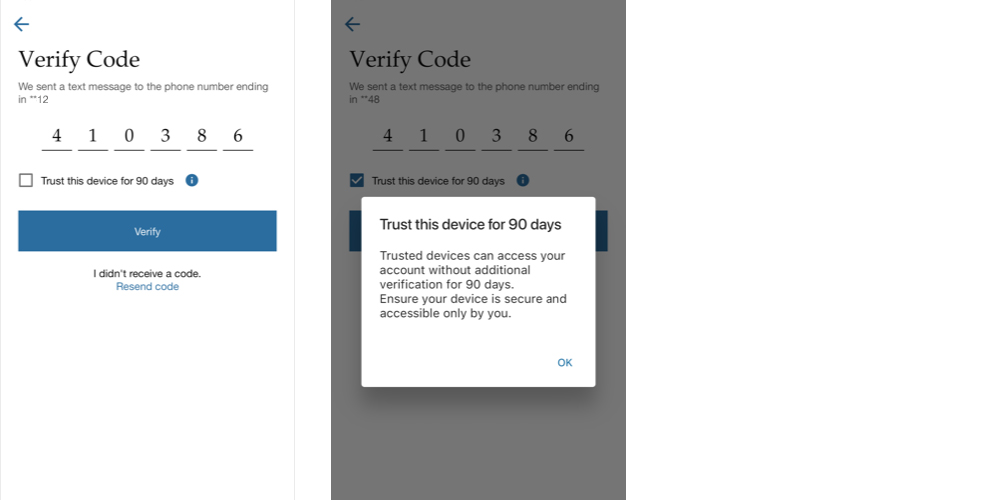
You should be aware of the following risks of trusting a device:
Lost or Stolen Device: If your trusted device is lost or stolen, whoever finds or steals it could potentially access your accounts without needing additional verification.
Physical Access by Unauthorized Individuals: If someone gains physical access to your trusted device without your consent, they could potentially access your accounts without needing additional verification.
Shared or Public Devices: Trusting a device that is shared with others or using a public computer poses risks, as others may gain unauthorized access to your accounts if they can use the trusted device.
Malware or Virus Infection: If your device becomes infected with malware or viruses, it could compromise the security of your accounts, especially if the malware steals passwords, intercepts authentication codes or gains access to sensitive information.
Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks: Logging into accounts from a trusted device on unsecured Wi-Fi networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots, increases the risk of interception and unauthorized access by malicious actors.
Outdated Software: Using a device with outdated software or unpatched security vulnerabilities increases the risk of exploitation by attackers, potentially compromising the security of trusted devices.
Note: If you suspect your credentials have been compromised, it's important to revoke the trust status of your devices and take steps to secure your accounts, such as changing passwords, enabling additional security measures on your device, and notifying relevant authorities if necessary.
To revoke the trust status of a device, simply disable MFA then re-enable. All your previously trusted devices will no longer be considered trusted.
